
Porcelain tile is a mixture of kaolin clays (40-50%), feldspar(20-30%), silica (15-25%), and mineral additives (5-15%) by pressing 1700psi and heating between 1200°C to 1400°C temperature of 22 hours of time. Porcelain tiles are high-density, brittle and harder material due to high compressing and burning.
Porcelin tiles are mainly 6 types according to their hardness, density, surface quality, and manufacturing methods. Those 6 types are glazed porcelain tile, unglazed porcelain tile, polished porcelain tile, matte porcelain tile, textured porcelain tile and semi-polished porcelain tile.
Kaolin clays, feldspar, silica, and mineral additives are the materials for porcelain tiles. Porcelain tiles are manufactured in main 11 steps main steps such as material procurement, blending and grinding, spray drying, pressing, glazing, burning, cooling, sorting and inspection, cutting and size, polishing and packaging.
The water absorption rate, coefficient of friction rate, density and hardness, tile porosity, breaking strength, PEI, quality of glaze, visual quality, and resistance are the main quality measurements of porcelain tiles. Due to these quality measurements, porcelain tiles are used for indoor and outdoor, domestic and commercial purposes.
Porcelain tiles have both advantages and disadvantages. Therefore before using a porcelain tiles, you should know the benefits and risks of the porcelain tiles. Although porcelin tile is a type of ceramic tile, it is better than ceramic tile due its high density, less water absorption, resistance, design finish, breaking strength, UV resistance, and uniformity.
What are the 6 Types of Porcelain Tiles?

The 6 types of porcelain tiles are glazed porcelain tile, unglazed porcelain tile, polished porcelain tile, matte porcelain tile, textured porcelain tile and semi-polished porcelain tile. Porcelain tile types are categorised by considering their durability, moisture resistance, and elegant appearance. Below are the 6 types of porcelain tile and their specific properties.
- Glazed Porcelain Tiles
- Glazed porcelain tiles have a liquid glass coating or a glaze on their surface. The glaze provides an aesthetic finish and can make the tile more stain-resistant. Therefore glazed porcelain tiles are available in a vast range of designs, colors, and textures due to the versatility of glazing.
- Unglazed (Full-bodied) Porcelain Tiles
- The unglazed porcelain tile colour is consistently spread through the entire thickness of the tile. Unglazed porcelain tiles are more robust and wear-resistant than glazed tiles. Therefore these tiles are commonly used in high-traffic areas.
- Polished Porcelain Tiles
- The polished porcelain tile surface is polished to a higher shine. Polished porcelain tiles reflect light well and have a sleek, modern look.
- Matte Porcelain Tiles
- Matte porcelain tiles have a subdued, non-shiny finish. Matte porcelain tiles provide better slip resistance than polished porcelain tiles.
- Textured or Structured Porcelain Tiles
- These tiles have a textured surface, which can replicate the feel of natural stone, wood, fabric, etc. Due to the texture of the structured porcelain tiles, they are wear-resistant and have a elegant aesthetic look.
- Lappato (Semi-Polished) Porcelain Tiles
- Lappato porcelain tiles are semi-polished. Lappato porcelain tiles have a soft glow and a slight reflection, offering a balance between polished and matte tiles.
How is Porcelain Tile Made?
The porcelain tile is made using kaolin clays (40-50%), feldspar(20-30%), silica (15-25%), and mineral additives (5-15%) with mixing of suitable proportions. The main steps of porcelain tile manufacturing are raw material procurement, blending and grinding, spray drying, pressing, glazing, burning, cooling, sorting and inspection, cutting and size, polishing and packaging. Each step has specific output, values and reasons.
- Raw Material Procurement: The primary ingredients used to manufacture porcelain tiles include clay (usually kaolinite clay), feldspar, sand (silica), and other natural minerals.
- Blending and Grinding: These raw materials are first blended and ground into a fine powder. Water is added to this powder to create a paste called “slip.”
- Spray Drying: The slip is then spray dried, a process that removes excess moisture and results in a fine, granulated powder.
- Pressing: This granulated powder is pressed under high pressure to form the raw tile shape. This is typically done using hydraulic presses of 1750 psi. The pressure compacts the powder, giving the tile its initial form and density.
- Glazing (Optional): Not all porcelain tiles are glazed. However, if a glazed finish is desired, the tile is coated with a liquid glass mixture before being fired. This glaze can be colored or decorative, and it melts to a smooth, hard, protective finish during firing.
- Bruning: The tile is then fired in a kiln at extremely high temperatures (typically around 1200°C to 1400°C). This firing vitrifies the tile, making it dense and strong. The firing process will take about 22 hours.
- Cooling: After firing, the tiles are cooled slowly. This controlled cooling helps in preventing the tiles from cracking or warping.
- Sorting & Inspection: Once the tiles have cooled, they are inspected for quality.
- Cutting & Sizing (Optional): Some tiles are rectified, which means they are cut or ground to precise dimensions after firing. This process ensures that all tiles are uniform in size.
- Polishing (Optional): Some porcelain tiles, especially those for indoor use, may be polished for a shiny finish.
- Packing & Shipping: Once the tiles pass inspection, they are packed in boxes and prepared for shipping to distributors, retailers, or job sites.
What are the Quality Measurements of Porcelain Tile?
The quality measurements of porcelain tile are water absorption rate, coefficient of friction rate, density and hardness, tile porosity, breaking strength, PEI, quality of glaze, consistency, edge quality, visual quality, resistance for stain, chemical thermal and fade. Quality measurement is important in selecting the proper tile for the specific place.
- Water Absorption Rate:
- High-quality porcelain tiles have a very low water absorption rate of less than 0.5%. This makes them frost-resistant and ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- Coefficient of Friction:
- This determines the slip resistance of the tile. For areas like bathrooms, you’d want a higher coefficient for safety.
- Density and Hardness:
- The denser and harder the tile, the more durable and resistant to wear and tear it is.
- Tile Porosity:
- Tiles are classified based on their porosity (from impervious to highly porous). High-quality porcelain is usually impervious or very low porosity, indicating that it resists moisture well.
- Breaking Strength:
- High-quality tiles should be able to withstand a significant amount of force before breaking.
- PEI (Porcelain Enamel Institute) Rating:
- Tiles are rated from PEI I (light traffic) to PEI V (heavy-duty traffic). Depending on where you’re planning to install the tile, you’ll want to consider its PEI rating.
- Quality of Glaze (if applicable):
- The glaze should be evenly applied without pinholes or bubbles, and it should be resistant to scratches and stains.
- Consistency in Size and Shape:
- High-quality tiles will have a consistent size and shape, allowing for tighter and more uniform installation.
- Edge Quality (if rectified):
- Rectified tiles have been mechanically finished to achieve uniformity and precision. The edges should be perfectly straight.
- Visual Aesthetics:
- The design, color, and pattern should be consistent from tile to tile, without noticeable discrepancies.
- Resistance to Chemicals and Stains:
- Quality porcelain tiles should resist most household chemicals and stains.
- Thermal Shock Resistance:
- It indicates how well the tile can withstand sudden temperature changes.
- Fade Resistance:
- The color and design of the tile should remain consistent even when exposed to sunlight over time.
What are the Uses of Porcelain Tiles?
Porcelain tiles are high hardness, higher durability, high slip resistance, and lower water absorption rate. Hence porcelain tiles are used for both indoor and outdoor applications in both domestic and commercial locations.
- Indoor Flooring:
- Living rooms and bedrooms
- Kitchens
- Bathrooms
- Hallways and entryways
- Wall Applications:
- Kitchen backsplashes
- Bathroom walls
- Feature walls in living areas
- Outdoor Applications:
- Patios and decks
- Walkways and pathways
- Pool areas
- Exterior walls and façades
- Countertops:
- Kitchen countertops
- Bathroom vanities
- Commercial Spaces:
- Offices
- Retail stores
- Restaurants
- Stairs
- Fireplace Surrounds
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Porcelain Tiles?
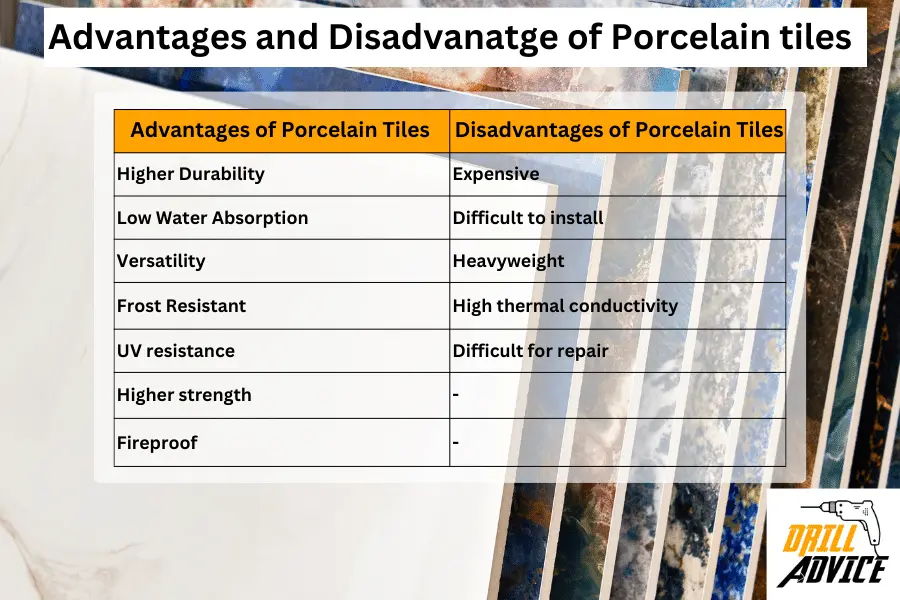
The advantages of porcelain tiles are due to its durability, low water absorption, versatility, resistance and higher strength. Each advantage have benefits which are mentioned below. Disadvantages of porcelain tiles are due to its material price, brittleness, high weight, thermal conductivity and higher hardness. Each of these disadvantages has a risk of using porcelain tiles.
Advantages of Porcelain Tiles
- High Durability – The tile surface is higher resistant to wearing and tearing
- Low Water Absorption – Water absorption is less than 0.5%. Hence porcelain tiles are good for wet areas.
- Versatility – Wide range of types and products are available
- Stain Resistant – Glazed porcelain tiles are stain resistant than other types of porcelain tiles.
- Frost Resistant – Porcelain tiles are suitable for use in outdoor areas in cold climates.
- UV resistance – Porcelain tiles are not fade in sunlight
- Higher strength – Higher breaking resistance
- Fireproof – Non-combustible and doesn’t exhaust any toxic fumes in a fire.
Disadvantages of Porcelain Tiles
- Expensive – Porcelain tiles are more expensive than ceramic tiles.
- Difficult to install – Due to high brittleness, porcelain tiles are difficult to cut and install.
- Heavyweight – Porcelain tiles are heavier than same-size ceramic tiles
- High thermal conductivity – Porcelain tiles can transfer heat easily.
- Difficult for repair – When replacing a single tile can affect the surround tiles badly.
Why is Porcelain Tile Better than Ceramic Tiles?
Porcelain tiles are better than ceramic tiles due to these 8 reasons such as.
- Porcelain tiles have higher density and durability than ceramic tiles
- Porcelain tiles have less water absorption rate than ceramic tiles.
- Porcelain tiles have higher frost resistance than ceramic tiles.
- Porcelain tiles have higher stain resistance than ceramic tiles.
- Porcelain tiles have a variety of designs and finishes than ceramic tiles.
- Porcelain tiles have stronger breaking strength than ceramic tiles.
- Porcelain tiles have higher UV resistance than ceramic tiles.
- Porcelain tiles have Uniformity than ceramic tiles
