
Wood is a widely used construction material. Wood is mainly 4 types according to heartwood, density and strength. All woods have different properties. The properties are important when selecting a wood. Wood should be treated to extend timber life and prevent insect attacks and fungal decays. Mainly wood is used for furniture and roof. The usage of the wood is varied with the strength and workability of the wood. Wood defects can reduce the quality and strength of the wood. It can be damaged by human, animal and environmental activities. But it can protect using coatings and sealants.
Wood is mainly 4 types. Those are softwood, hardwood, engineered wood and exotic wood. Wood has categorised into main 4 types according to the heartwood, density and strength of the wood. The denser area of the wood is named as heartwood. The lower dense area is sapwood. Denser woods are less workable but more durable, with less damage and defects.
Wood is processed to lumbers in mainly 4 methods. Those are live-sawn, plain-sawn, quarter sawn and rift sawn. Live-sawn is the lowest waste-generated method. Plain sawn is the most used method for lumber cutting. Rift sawn is a complicated method of lumber cutting. Quarter-sawn provides stronger lumbers but it is more expensive.
Wood characteristics and behaviours are based on the wood’s properties. The main 10 properties of the wood are wood strength, structure, density, specific gravity, knots, grain, colour, growth rings and water content. Each of these properties directly affects the strength, stability and quality of the wood. Therefore these properties are useful in wood selection.
Wood should be treated before using it. Wood treatments can improve mainly these 03 things such as durability, insect resistance, and strength. The main 3 types of treatments are pressure treatment, chemical treatment, and heat treatment. Pressure-treated and chemically treated wood is long lasting about 10-40 years, and heat-treated wood will last long about 15-30 years. The usage of the wood varied with the hardness of the wood. Softwood is used for furniture, packaging, paper and pulps and door and windows mainly. Hardwood is used for furniture, flooring, and musical instruments mainly.
Wood has defects. Those defects are considered as any abnormality or irregularity found in the structure or appearance of wood. The main 5 wood defects are knots, checks, splits, warping, and rotting. Defects are formed during the tree growth period and various environmental conditions. Defects can reduce the strength and stability of the wood. Small defects can be fixed by using fillers or epoxy resins easily. But larger defects need more filling, cutting and sanding processes.
Due to the defects and user behaviours, wood damage are occurred. Mainly wood is damaged by insects, environments, physical impacts, radiation and chemical damage. You can protect the wood mainly by doing regular cleaning, moisture control, pest prevention, and regular maintenance.
What Are the Types of Wood?
The main 4 types of wood are hardwood, softwood, engineered wood and exotic wood. Hardwood is denser than other wood and it is more durable. Softwood is lightweight and easy to work with. Engineered woods are man-made wood using wood particles. Exotic wood is not native to North America.
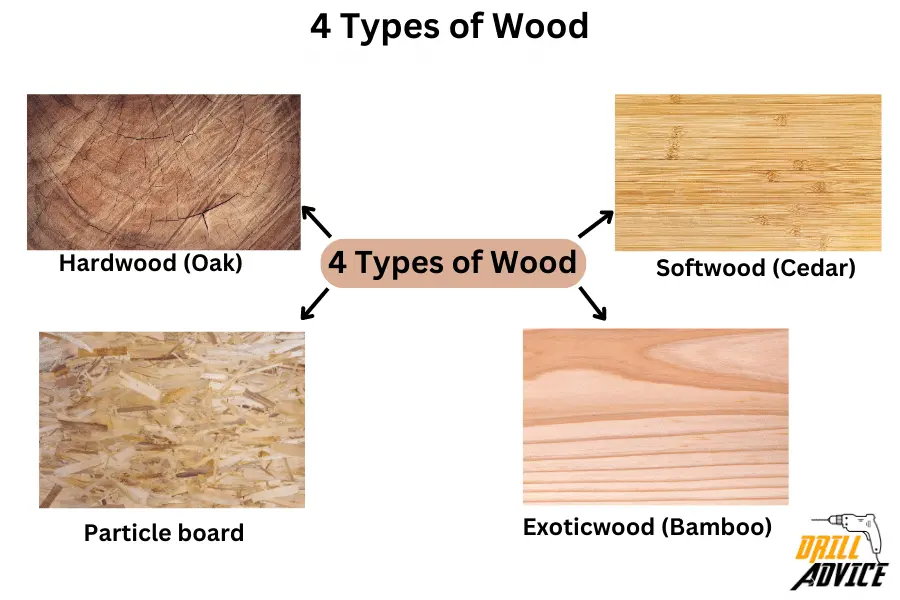
1. Hardwood
Hardwoods are usually denser and more durable. There is a wider heartwood than sapwood. Therefore hardwood is more resistant to water and heat. Hence hardwood is more durable. The workability (cutting and drilling) of the hardwood is difficult due to dense heartwood.
These are the 6 most used hardwoods in the USA.
- Oak: There are several types, including red and white. It’s strong and durable with a distinctive grain. Often used for furniture, flooring, and barrels.
- Maple: Maple is hard and durable. It’s often used for heavy-use items like bowling pins and baseball bats etc. Maple is also a popular choice for furniture and flooring.
- Cherry: Cherry is known for its rich, reddish-brown color and straight grain. It’s softer than oak and maple but is often used for fine furniture, cabinetry, and decorative items.
- Walnut: Walnut has a rich dark color look. Walnut has a strong heartwood but it is easy to work. Therefore walnut is used to make furniture and decorative veneers.
- Mahogany: Known for its reddish-brown color and fine grain. It’s somewhat soft for a hardwood, but is still durable. Mahogany is used for making furniture, paneling, and musical instruments.
- Teak: Teak is highly durable and resistant to decay. It is used for outdoor furniture and boat decks. It’s also used in high-end indoor furniture and flooring.
The most popular hardwood are Birch, Poplar, Beech, Ash, Hickory, Alder, Rosewood and Elm.
2. Softwoods
Softwoods are generally lighter and less dense than hardwoods. They come from coniferous trees, which typically remain evergreen in the year.
These are the 5 most used hardwoods in woodworking.
- Pine: Pines have many varieties, such as white, yellow, and ponderosa. It’s light, soft, and easy to work with. Often used for furniture, panelling, and construction.
- Cedar: Light, soft, and aromatic. Known for its natural resistance to decay, it’s often used for outdoor furniture, decking, and shingles.
- Fir: Also known as Douglas fir, it’s hard for softwood and is often used in construction for things like framing and plywood.
- Spruce: Spruce is light and soft. It’s often used in construction and for making musical instruments, particularly soundboards for pianos and acoustic guitars.
- Redwood: Renowned for its resistance to decay and insects, it’s a popular choice for outdoor structures like decks and garden furniture.
3. Engineered Woods
These are man-made products, often made from wood fibers or veneers bonded together.
These are the stronger engineered woods.
- Plywood: Plywood is made from thin layers of wood glued together. It’s strong and durable and is used in everything from furniture to house construction.
- MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard): Made from wood fibers glued under heat and pressure. It’s often used for furniture and molding.
- Particle Board: Made from wood particles glued together. It’s less expensive and less durable than other types of engineered wood and is often used in inexpensive furniture.
- OSB (Oriented Strand Board): Similar to particle board, but made with larger pieces of wood. Often used in construction.
4. Exotic Woods
These are from trees that are not native to North America.
The 4 most popular exotic woods are;
- Ebony: A very dense and dark hardwood, it’s often used for small ornamental purposes.
- Rosewood: Known for its strong grain and sweet smell, it’s often used in making musical instruments and fine furniture.
- Balsa: Despite being a hardwood, balsa is extremely light and soft. It’s often used for light, stiff structures such as model airplanes.
- Bamboo: While technically a grass, bamboo is often included in discussions of wood. It’s strong, lightweight, and grows quickly, making it a sustainable choice for flooring and furniture.
Read More about – 22 Wood Types: Hardwood, Softwood, Engineered Wood and Exotic Wood
What Are the Types of Wood Cuts?
The most used 4 types of woodcuts are live sawn, quarter sawn, rift sawn, and plain sawn. These woodcuts are used to slice the lumber with different grain patterns and strengths. According to the lumber and grain pattern, its workability will be varied. Uniform grain patterns can improve the strength of lumber. When the lumbers are sawing using wood, there is an excess material. These are called waste. Lumber cutting need labour and tool. Therefore each cut has a cost and waste. The aim of wood cutting is less waste and cost-effective lumber.
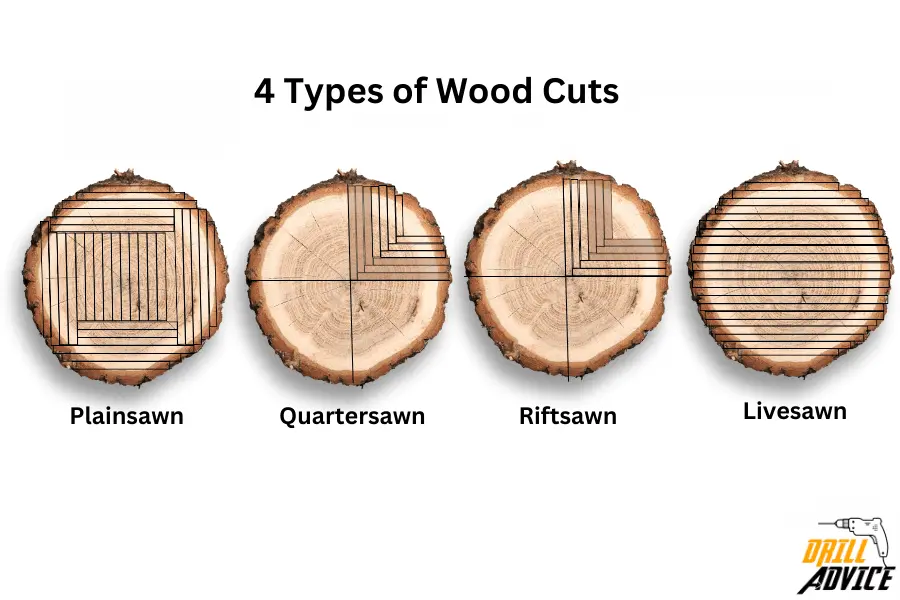

1. Live Sawn
Live sawn is the lowest waste generation in lumber sawing. It is a cost-effective sawing method. This method involves cutting straight through the log from one side to the other. Therefore each board contains a mix of grains. Strength and stability is less than the plain sawn and quarter sawn. Live sawn is more efficient than a quarter and rift sawing.
2. Plain Sawn
This is the most common method of cutting lumber. The log is simply cut from one end to the other in parallel slices. The grain pattern of the plain sawn is broad and wavy. Therefore it is more unique and aesthetic. The strength of the plan sawn is less than the other sawing methods. Therefore it can cupping and twisting easily.
3. Quarter Sawn
This method involves cutting the log into quarters and then sawing perpendicular to the growth rings. Therefore it need more time and produces more waste. The workpiece is more stable and stronger than other swans. The grain is straighter and tighter. Therefore it is resistant to warping and cupping.
4. Rift Sawn
Rift sawing is the most labour-intensive and least-used method. The log is first quartered, and then each quarter is cut at a different angle to the growth rings (usually around 45 degrees). This produces a very straight and uniform grain pattern, which is highly desirable for certain applications. It also produces the most stable wood, with the least likelihood of warping or cupping.
What are the Properties of Wood?
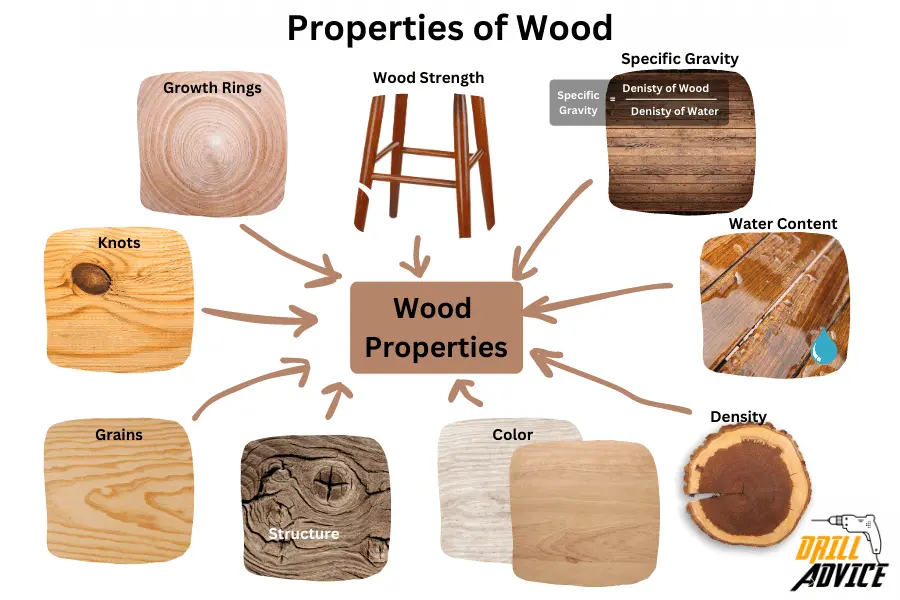
1. Wood Strength
Wood strength is the ability of wood to withstand external forces without breaking or deforming. The strength of wood depends on multiple factors such as the species of the tree and the specific part of the wood being used. Heartwood is the stronger part of the wood.
The strength of wood directly affects its workability. Stronger woods require more effort and sharp tools to cut and drill effectively. Stronger woods are suitable for durable, more load-bearing and wear and tear-resistant projects such as constructing furniture, flooring, or structural components.
Softwoods like pine and cedar, while not as strong as hardwoods, offer excellent workability and are commonly used in projects that require intricate detailing or ease of carving. Therefore these woods can be easily shaped and require minimum power when using power tools.
2. Wood structure
The wood structure is the arrangement of cells, grains, and knots in the wood. The structure has a significant impact on both the strength and workability of the wood. The arrangement of grains and the presence of knots affect the overall stability and aesthetic of the wood.
The grains in wood is the longitudinal fibers that run parallel to the tree trunk. Woods like ash or maple,have a straight and consistent grain. Therefore, these are higher strength and stability. Hence these woods are used for durable woodwork projects.
3. Wood Density
Wood density is considered as the mass of wood per unit volume. Different parts of a tree has various densities. The inner part is named heartwood. Heartwood is denser than the outer sapwood. The density of the wood affects the strength, durability, and workability of the wood.
Dense woods, such as oak or ebony, offer increased resistance to wear and tear; therefore, those are used for durable furniture. Dense woods need more effort, workability and specialized tools to cut and drill effectively. Power tools used on dense woods may need more power and can experience faster tool wear.
Less dense woods, like balsa or pine, are easier to work with due to their lower density. They require less power and cause less strain on power tools during cutting and drilling. However, these woods may be more susceptible to dents, scratches, and general wear.
4. Wood-Specific Gravity:
Specific gravity is the ratio of the density of wood to the density of water. Higher specific gravity indicates denser wood, while lower specific gravity represents less dense wood. For example, woods like ebony and ironwood have higher specific gravity. In contrast, woods like cedar and spruce have lower specific gravity, making them lighter and more suitable for projects that require ease of handling.
Specific gravity affects the overall characteristics of wood, including its strength, workability, and resistance to moisture. Woodworkers must understand how specific gravity influences these factors to choose the most appropriate wood for their projects.
5. Wood Knots:
Wood Knots are areas in the wood where branches once grew. This is happened naturally during the tree’s growth process. Knots can have both advantages and disadvantages in woodworking. Small, tight knots can add aesthetic appeal and uniqueness to the finished piece without significantly compromising strength or workability. In contrast, large knots can weaken the wood, making it prone to splitting or warping.
Woodworkers often employ techniques to stabilize knots or remove them entirely. By strategically incorporating or avoiding knots, woodworkers can enhance the workability and strength of their projects.
6. Wood Grain:
Wood grain is the texture and pattern of wood fibers visible on the surface of a piece of wood. It is formed by the direction in which the tree’s fibers grow. The grain pattern can be classified into three main types: straight grain, interlocked grain, and spiral grain.
Straight-grain woods, such as maple or oak, have fibers that run parallel to each other, resulting in a uniform and consistent appearance. They tend to exhibit greater strength and stability, making them suitable for applications that require durability and load-bearing capacity.
Interlocked grain woods, like mahogany or teak, have fibers that intertwine irregularly. This unique grain pattern contributes to the wood’s beauty but can also pose challenges during cutting and drilling. Interlocked grains in wood can be splinter or tear. Therefore it requires careful tool selection and technique to achieve the results.
Spiral grain woods, such as pine or spruce, have fibers that twist or spiral as they grow. This grain pattern can result in an interesting visual effect but may also impact workability. Spiral grain wood can be prone to warping or distortion, requiring extra attention during cutting and drilling.
7. Wood Color:
The color of the wood is determined by the natural pigments present in its cells. Various factors, The color variation depends on these factors such as tree species, growing conditions, and age of the wood.
Different wood colors can be utilized to identify specific wood types. For example, the reddish-brown hue of mahogany or the pale yellow color of pine can help distinguish one wood species from another. In some cases, wood color can be improved or enhanced through staining or finishing techniques, allowing woodworkers to achieve specific aesthetic preferences.
However, it’s important to note that wood color can be susceptible to damage or fading when exposed to sunlight or harsh environmental conditions. Proper protective measures, such as using UV-resistant coatings or keeping the wood away from direct sunlight, can help preserve and maintain the desired color of the wood.
8. Wood Growth Rings:
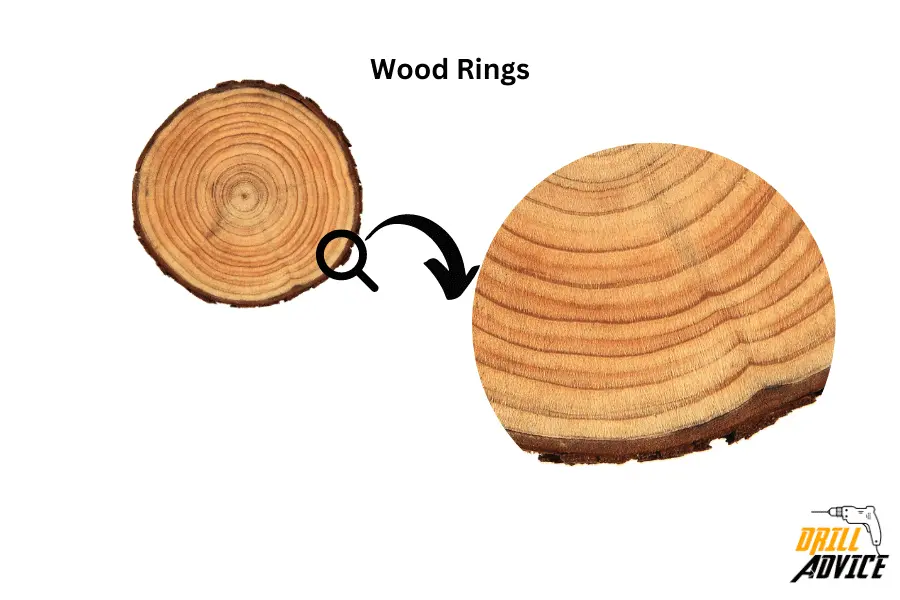

Wood growth rings are concentric circles visible on the cross-section of a tree trunk. Each growth ring represents one year of growth. The growth rings consist of two distinct parts: the lighter-colored springwood and the darker-colored summerwood.
The growth rings add more aesthetic look to the wood products. The contrasting colors and patterns created by the growth rings can add visual interest and uniqueness to woodworking projects, such as furniture or decorative items.
The growth ring can affect the properties of the wood such as density, strength, and stability of the wood, influencing its workability and suitability for specific applications.
9. Wood Water Content:
Wood water content refers to the amount of moisture present in the wood fibers. Freshly cut or “green” wood typically has a high water content, which can significantly affect its properties. High water content can lead to wood swelling, warping, or even decay. Therefore, it is essential to reduce the water content of the wood through a process known as wood drying or seasoning.
Wood drying is removing excess moisture from the wood to achieve a suitable counterbalance with the surrounding environment. This process can be done through air drying or kiln drying methods. Properly dried wood has a lower water content. Therefore those have good stability, strength, and workability.
Wood treatments, such as applying sealants or wood preservatives, can further protect the wood from excessive moisture absorption and subsequent damage. These treatments create a barrier that helps maintain the wood’s desired moisture content, ensuring its long-term durability and workability.
What is Wood Treatment?
Wood treatment is a process which is applying certain substances to the wood to improve its durability, resistance to decay, and overall lifespan. The main 3 methods of wood treatment are pressure treatment, chemical treatment, and heat treatment.
Wood treatments can have a significant impact on the workability of wood pieces. Treated wood is more stable, less prone to warping, and better protected against insect damage and fungal decays.
The duration of wood treatment depends on the specific method used and the desired level of protection. Pressure-treated woods can long lasting about 10 – 50 years. Chemical-treated wood will long last about 10- 40 years and heat-treated wood will long last about 15-30 years.
The advantages of wood treatment include increased durability, extended lifespan, and improved resistance to environmental factors. However, it’s important to note that some wood treatments may alter the appearance or color of the wood, and certain chemical treatments may introduce potential health and environmental concerns.
What is the Usage of Wood?
Mostly wood is used for making furniture and construction homes. The usage of the wood is varied with its properties such as heartwood, density, colour, strength, durability, grain pattern, and stability. Each tree provide different types woods with properties.
These are the 10 most used wood for different purposes.
- Pine – Pine is a softwood. That is light, durable, and easily worked, ideal for furniture, paneling, and construction framing.
- Oak – Oak is a hardwood. Oak is highly resistant to wear, with beautiful grain patterns. It’s used in flooring, furniture, and timber frame buildings.
- Maple – Maple is hardwood. It is often used for heavy-duty items like butcher blocks and bowling pins.
- Cherry – Cherry is a fine grain and warm, rich color. It is used for furniture, veneer, and cabinetry.
- Cedar – Cedar is aromatic and naturally resistant to rot and pests. Therefore, cedar is used for outdoor furniture and fencing.
- Teak – Due to its high oil content, teak is incredibly durable and resistant to water and pests. It’s used for outdoor furniture, boat decks, and other marine applications.
- Mahogany – Mahogany has dark rich color and straight grain. Therefore mahogany is used for high-quality furniture, musical instruments, and boat interiors.
- Walnut – Walnut wood is strong, hard, and durable, with a rich color that makes it a top choice for furniture, flooring, and veneers.
- Ash – Ash is a tough wood. Therefore it is used for tools, sports equipment, and for high-quality furniture.
- Birch – It’s heavy, strong, and durable, making it suitable for furniture, plywood, and veneers. Birchwood is also used for crafting musical instruments due to its resonance qualities.
Read More About – 13 Types of Wood Joints: Techniques, Strength, Visibility, Pros, and Cons
What is a Wood Defect?

A wood defect can be considered as any abnormality or irregularity found in the structure or appearance of wood. These defects can occur naturally during the tree’s growth or can result from external factors, such as damage during harvesting or processing. There are 10 types of wood defects can be seen in the wood.
10 Types of Wood Defects:
- Knots
- Checks
- Splits
- Warping
- Rot
- Wane
- Decay
- Pitch Pockets
- Blue Stain
- Honeycombing
How is Wood Defect Forming?
Wood defects are formed due to several factors. Knots is occur due to part of the tree trunk. Splits and shakes can occur when the wood undergoes excessive drying or exposure to extreme temperature variations. Environmental conditions, such as high humidity, can lead to warping and twisting of the wood.
What are the Impact of Defects for the Strength and Quality of the Wood?
Wood defects can significantly affect the strength and quality of wood products. They can weaken the structural integrity, reduce load-bearing capacity, and impair the overall appearance. For example, a large knot in a load-bearing beam can compromise its strength, making it susceptible to failure. Defects can also lead to uneven staining, hinder the finishing process, and affect the wood’s dimensional stability.
How to Fix Wood Defects?
Addressing wood defects requires careful consideration and appropriate techniques. Minor defects can often be repaired with wood filler or epoxy resin. Larger defects may necessitate cutting out the affected portion and replacing it with a patch. In some cases, strategic repositioning or cutting techniques can minimize the impact of defects during woodworking projects.
How is Wood Damaged?
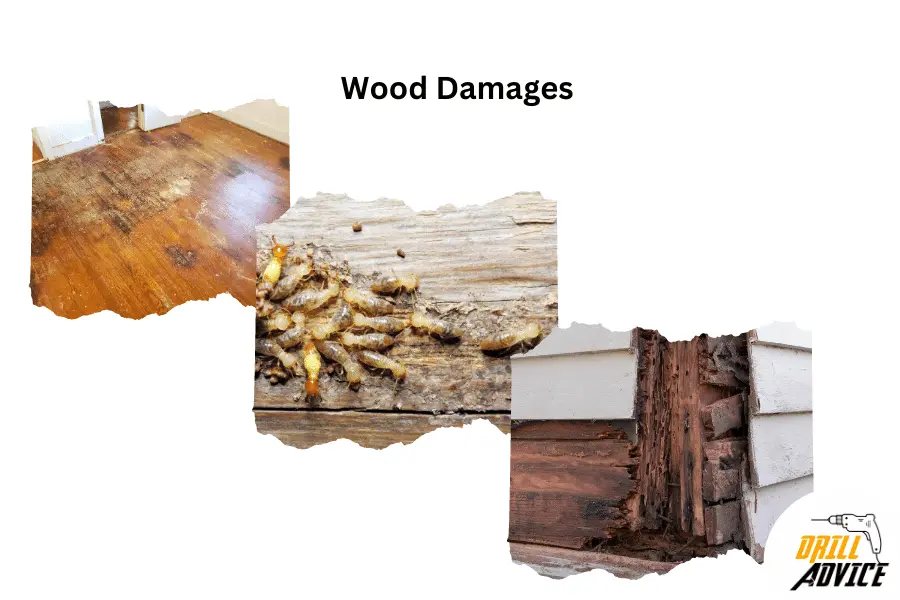

Damaged wood is considered as wood that has undergone physical, chemical, or biological changes, negatively impacting its structure, strength, and aesthetic qualities. Wood damage can manifest in various forms, such as decay, insect infestation, mechanical damage, or weathering.
What are the Reasons for Wood Damages?
- Moisture and Humidity – Prolonged exposure to moisture and high humidity levels can lead to rot, mold, and mildew growth, compromising the wood’s integrity.
- Insects and Pests – Wood-boring insects, termites, and beetles can burrow into the wood, causing structural damage and weakening its strength.
- Physical Impact – Accidental impacts, excessive force, or improper handling can result in dents, scratches, cracks, or splintering.
- UV Radiation – Sunlight exposure over time can cause discoloration, fading, and surface degradation of the wood.
- Chemical Damage – Harsh chemicals, solvents, and acids can erode the wood’s surface, leading to deterioration and weakening of the material.
How to Protect Wood?
Applying Sealants and Coatings: Sealants and Coatings are essential to protect wood from elements like moisture and UV radiation. The most used sealant and coating are polyurethane, varnish, or penetrating oils. The usage depends on the specific wood type and usage.
- Regular Cleaning – Consistent cleaning helps eliminate accumulated dirt, dust, and debris, which can potentially damage the wood over time.
- Moisture Control – To prevent moisture damage, wood items should be kept away from damp areas.
- Avoiding Direct Sunlight – Overexposure to direct sunlight can cause wood to fade and degrade. Therefore keep away wood items from windows, using curtains, blinds, or UV-filtering films. You can apply UV-protective coating can help in sunlight mitigation.
- Pest Prevention – Pest preservation can be controlled by regular inspection of the wood item. If there is any crack on the floor of any pest hazard, you should keep away the wood item.
- Avoiding Excessive Weight or Force – Excessive weight, force, or impact can cause damage to wood. It’s advised to use proper lifting techniques when moving heavy wooden items and to place protective pads under furniture legs to prevent scratches.
- Regular Maintenance – Routine maintenance includes inspecting wood surfaces regularly for signs of damage, prompt repairing using appropriate techniques, and regular tightening of screws, hinges, or joints to ensure structural integrity.
