
Ni-Cd (Nickle-Cadmium) battery is a rechargeable battery. Ni-Cd battery chemistry is nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes. The most popular Ni-Cd batteries are AA and AAA with 1.2 voltage. Due to the small size and voltage, Ni-Cd batteries are widely used in small electric equipment. The Ni-Cd battery was invented by Waldemar Jungner of Sweden in 1899. Below are the most important properties of Ni-Cd batteries.
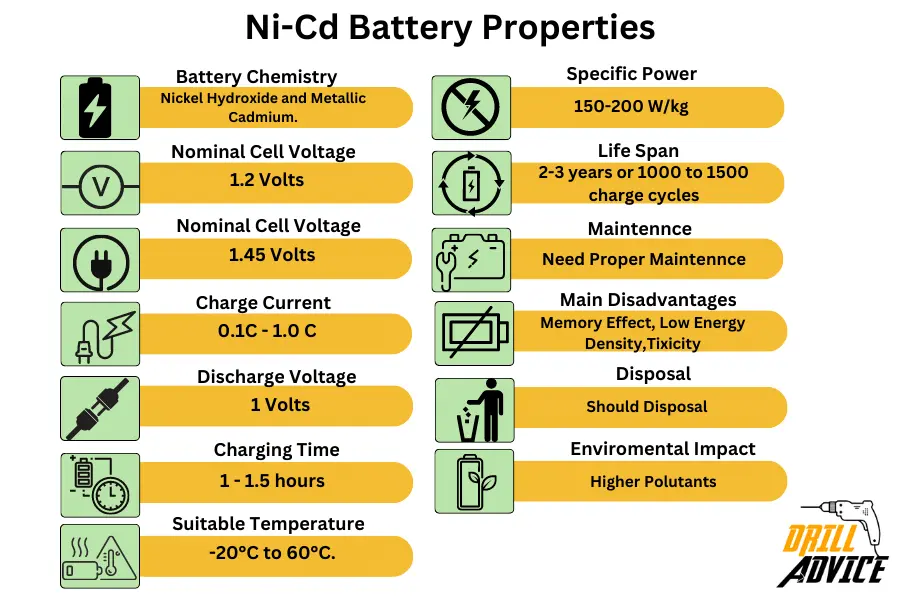
- Battery Chemistry: Ni-Cd batteries involve a chemical reaction between nickel hydroxide and metallic cadmium.
- Nominal Cell Voltage: Ni-Cd batteries have a nominal voltage of 1.2 volts.
- Charge Voltage: A typical Ni-Cd battery has a charge voltage of around 1.45 volts.
- Charge Current: Ni-Cd batteries usually support a charge current of 0.1C to 1.0C.
- Discharge Voltage: The discharge voltage for these batteries can drop down to 1.0 volt.
- Charging Time: Generally, Ni-Cd batteries take about 1-1.5 hours to charge.
- Suitable Temperature: Ni-Cd batteries operate best between -20°C to 60°C.
- Specific Power: Ni-Cd batteries typically have a specific power of 150-200 W/kg.
- Lifespan: The life of a Ni-Cd battery can span between 2-3 years or 1000 to 1500 charge cycles.
- Maintenance: Proper maintenance includes deep cycling, avoiding overcharging, and proper storage.
- Applications: Ni-Cd batteries are used in power tools, emergency lighting, aviation, etc.
- Disadvantages: Susceptibility to the ‘memory effect’, lower energy density, and containing toxic cadmium are notable drawbacks.
- Disposal: Ni-Cd batteries should be taken to a recycling facility or designated drop-off point.
- Environmental Impact: Cadmium in Ni-Cd batteries can cause environmental and health issues if not properly disposed of.
What is the Battery Chemistry of Ni-Cd Battery?
Battery chemistry is the type of electrochemical reaction in the battery when it charges (store energy) and discharges (release energy). The nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) battery uses chemical reactions between nickel and cadmium to produce electricity.
On charging, the positive nickel oxide electrode undergoes the reaction.
- NiO(OH) + H2O + e− → Ni(OH)2 + OH− (This reduces nickel oxide to nickel hydroxide)
When it discharges at the negative cadmium electrode, the reaction
- Cd + 2OH− → Cd(OH)2 + 2e− (This reaction oxidizes cadmium to cadmium hydroxide)
The potential difference generated electron flow and current when it connected in a circuit. The alkaline electrolyte allows the transfer of hydroxide ions. Due to these reactions, Ni-Cd batteries have reliable performance, high discharge currents, and lack of memory effect if it fully discharged.
What is the Nominal Cell Voltage of Ni-Cd Battery?
The nominal voltage of a Ni-Cd battery is the approximate average voltage that the cell maintains during the regular discharge operation.
The nominal cell voltage of a Ni-Cd (Nickel-Cadmium) battery is typically 1.2 volts. This value represents the standard or ‘nameplate’ voltage of the battery cell under typical operating conditions.
What is the Charge Voltage of Ni-Cd Battery?
The charge voltage of a Ni-Cd battery is typically 1.4 – 1.5V per cell. This value can vary slightly depending on the manufacturer’s recommendations, the battery’s condition, and the battery temperature.
Charging to a lower voltage can lead to undercharging and capacity loss over time due to the memory effect. Charging a Ni-Cd battery at the correct voltage is important to optimize its performance and lifespan.
What is the Charge Current of the Ni-Cd Battery?
The standard charge current for Ni-Cd battery is the recommended optimal current for charging the battery under normal conditions according to international standards. The standard charging current of Ni-Cd battery is 0.2C to 1.0C (where 1C is the rated capacity of a cell in amp-hours).
If you use too high of a charge current during the charging of Ni-Cd battery, it can overheat the battery. It will not fully charged if you use too low current. Therefore you should always use an optimal level of charging current for the maximize the lifespan and performance of the Ni-Cd battery.
What is the Discharge Voltage of Ni-Cd Battery?
The discharge voltage of a Ni-Cd battery is the voltage of the battery during the process of discharging or using the battery to power a device/load. When a Ni-Cd cell is used to drive a load, its voltage will decrease from the fully charged voltage of 1.2V down toward the cut-off or minimum discharge voltage of 1.0 to 1.1V per cell.
What is the Charging Time of the Ni-Cd Battery?
The charging time of Ni-Cd battery is varied with the charging current, charging voltage, charging power, battery chemistry and battery temperature. If a Ni-Cd battery is charged with 1C, it will take 1-1.5 hours. If it charges 0.1C, it will take 10-15 hours. (where C is the capacity of the battery)
Using higher current Ni-Cd batteries can be charged fastly. But it can increase the temperature of the Ni-Cd battery and reduce the battery life.
What is the Memory Effect of Ni-Cd Battery?
The memory effect is the phenomenon where a battery seems to ‘remember’ its previous low state of charge and cannot deliver its full rated capacity. The memory effect can reduce overall capacity by up to 20% in extreme cases. It can be avoided by fully discharging the battery before recharging. Brand-new Ni-Cd batteries have the least memory effect.
For example, a Ni-Cd battery rated at 2000mAh may only deliver 1000mAh if repeatedly recharged after discharging to 50%.
For optimal performance and lifespan Ni-Cd batteries should fully discharge before charging to avoid any harmful effects of the memory phenomenon.
What is the Charge Discharge Rate of Ni-Cd Battery?
The charge and discharge rate of a nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) battery indicates how quickly it can be charged or discharged relative to its maximum capacity.
Ni-Cd batteries are typically charged at 0.1C to 0.3C rate, so 100-300mA for a 1000mAh battery. The recommended discharge rate is up to 1C or the rated capacity. So a 1000mAh Ni-Cd could provide up to 1A discharge current. But using too high of a charge/discharge rate can damage the battery.
What is the Cycle Life of Ni-Cd Battery?
The cycle life of a Ni-Cd battery is the number of complete charge-discharge cycles the battery can undergo before its capacity degrades below usable levels. The cycle life is considered as 70-80% of the original capacity. The cycle life depends on battery material composition, charging practices, and operating conditions
Ni-Cd batteries have 1000-1500 cycle life. Cycle life can be increased by proper maintenance and avoiding memory effect of the Ni-Cd battery. Higher capacity Ni-Cd batteries may deliver up to 1500 cycles.
What is the Suitable Temperature to Use Ni-Cd Battery?
The temperature of the Nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) battery is very important for higher performance, safety and a longer lifespan. Therefore Nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) battery should charge up to 50°C. It can use between -20°C to 50°C (-4°F to 122°F). It should store -20° to 50°C/-4° to 122°F when it is not in use.
Extreme heat or cold can negatively impact the battery’s charging and discharging capabilities. Therefore it can use recommended temperatures always.
What is the Specific Power of the Ni-Cd Battery?
Specific power is the power-to-weight ratio of a battery. It measures how much power in watts a battery can deliver per kilogram of weight. For nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries, the specific power ranges from 150 to 200 W/kg.
The specific power of a Ni-Cd battery depends on factors like electrolyte formulation, internal design, and electrode thickness.
What is the Lifespan of a Ni-Cd Battery?

The lifespan of a nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) battery depends on usage and maintenance factors. Ni-Cd batteries typically last 3-5 years or 1000-1500 charge/discharge cycles before capacity degrades to 80% of the original.
4 factors to maximize the Ni-Cd lifespan
- Avoid memory effect by fully discharging before recharging
- Use good quality chargers following manufacturer guidelines
- Operate within the recommended temperature range
- Prevent short circuits and physical damage
- Store in a cool, dry place when not in use
With careful use, larger Ni-Cd batteries may last up to 10 years. However, lifespan shortens with heavy use or abuse. On average, most consumers can expect around 1000-1500 cycles and 3-4 years from a well-maintained Ni-Cd battery.
How to Maintenance Better Ni-Cd Battery?

Ni-Cd batteries should be well maintained in order to have better performance and long life cycles. You can follow the below steps to maintain the Ni-Cd battery properly.
- Fully discharge batteries before recharging to avoid memory effects. Discharge to 0.9-1V per cell.
- Use the correct charger and follow manufacturer guidelines for optimal voltage and current.
- Do not leave batteries in chargers for over 48 hours as this can reduce lifespan.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place at around 40-50% charge state when not in use.
- Avoid short-circuiting batteries or exposing to high temperatures outside -20°C to 50°C.
- Periodically cycle batteries that are in storage to redistribute electrolytes.
- Check for damage to the casing and replace if needed.
- Clean battery contacts if dirty or corroded.
What Are the 9 Applications of Ni-Cd Battery?
Nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries are valued for their reliable performance, high discharge current capabilities, and long cycle life. Therefore Ni-Cd batteries are used in wide range of applications and use in different industries such as,
- Power tools – drills, saws, sanders, grinders
- Remote controlled toys and models
- Emergency lighting and backup power
- Portable electronic devices – Two-way radios, metal detectors, flashlights
- Cordless appliances – Vacuums, shavers, toothbrushes
- Aviation and aerospace – Aircraft starting batteries
- Backup power for data centers, telecom networks
- Electric vehicles – Forklifts, golf carts, scooters
- Medical devices – Defibrillators, infusion pumps
What Are the 11 Disadvantages of Ni-Cd Battery?
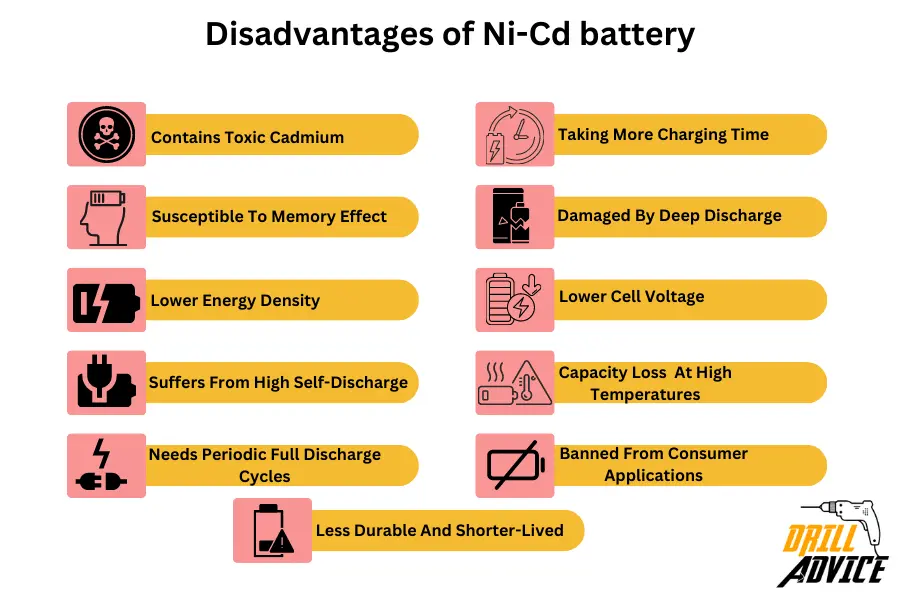
Ni-Cd batteries have disadvantages due to its improper physical and chemical behaviors. Below are the 11 most problematic disadvantages of Ni-Cd battery.
- Contains toxic cadmium – requires proper disposal and recycling
- Susceptible to memory effect if not fully discharged before recharging
- Lower energy density than Li-ion batteries
- Suffers from high self-discharge – up to 20% per month unused
- Needs periodic full discharge cycles to avoid electrolyte crystallization
- Charging typically takes 1-3 hours due to lower charge rates
- Can be damaged by deep discharge below 0.9V per cell
- Has lower cell voltage of 1.2V vs Li-ion at 3.6V
- Shows capacity loss if stored at high temperatures
- Banned from consumer applications in some regions due to cadmium
- Less durable and shorter-lived compared to Li-ion batteries
What are the 8 Alternatives for Ni-Cd Battery?
Ni-Cd batteries are toxic to the environment and human, has a memory effect, lower energy density, higher self-discharge rate, higher charging time, lower cell voltage, and capacity loss with time, and are banned from some countries. Therefore alternative battery is essential as a better power source. You can use the below batteries for the alternatives for the Ni-Cd batteries.
- Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) – No cadmium. Higher energy density but more expensive. Used in many consumer devices.
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) – Higher voltage, much higher energy density. Widely used in electronics.
- Lead-acid – Cheaper but very heavy. Used in automotive starting applications.
- Alkaline disposables – Zinc/manganese dioxide cells. Lower cost but not rechargeable.
- Lithium primary – Long shelf life with high energy density. Mostly non-rechargeable.
- Silver oxide – Expensive but high energy density. Used in medical devices.
- Rechargeable alkaline – Similar performance to Ni-Cd but no cadmium. Newer technology.
- Zinc-air – High specific energy. Still in development stage.
How to Disposal Ni-Cd Battery?
Due to the toxic cadmium content, Ni-Cd batteries must be recycled or disposed of responsibly, never in normal trash. Many retailers offer free battery recycling programs, accepting old rechargeable batteries like Ni-Cd.
You can also check if your local municipal waste department has a hazardous material collection for batteries. In some areas, manufacturers and importers of Ni-Cd batteries are required to provide free mail-back programs for recycling.
If no recycling options are available, you can contact your regional Environmental Protection Agency for guidance on disposing of hazardous household waste. When tossing or recycling Ni-Cd batteries, tape the terminals to prevent fires or short circuits. Responsible Ni-Cd battery disposal protects the environment and human health from cadmium pollution.
What are the Environmental Effects of Ni-Cd Batteries?

Ni-Cd batteries contain cadmium which is a toxic material for humans and the environment. Cadmium can pollute the environment by bioaccumulation in the food chain and affect the human lungs, livers, kidneys, and bones badly. NiCd batteries are non-biodegradable materials. It can remain in the environment if it is not properly recycled. A huge environmental impact occurs when a Ni-Cd battery is manufactured.
The 5 most harmful environmental effect of Ni-Cd are;
- Toxicity: Cadmium is a heavy metal that is highly toxic, especially when inhaled or ingested. Cadmium exposure poses risks of lung, kidney, liver, and bone damage in humans and animals. Fortunately, recycling programs allow Ni-Cd batteries to be disposed of responsibly. Many regions restrict or ban Ni-Cd batteries due to these environmental hazards. Overall, while useful, Ni-Cd batteries must be managed cautiously throughout their lifecycle.
- Pollution: Ni-Cd batteries leak into the soil and groundwater through landfill, it can then enter the food chain through plants and animals as a toxic compound.
- Bioaccumulation: Cadmium can accumulate in organisms over time, leading to detrimental effects on ecosystems, particularly aquatic ones.
- Non-Biodegradable: Ni-Cd batteries are not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for a long time if not properly recycled.
- Resource Depletion: The production of Ni-Cd batteries involves mining and refining of nickel and cadmium, which can lead to resource depletion and associated environmental impacts.
